Remote connections
Remote connections are a fully integrated feature of Nerve Blue. They are available in two flavors: remote screens and remote tunnels.
- Remote screens are connections that are established between the Management System and a target. They are visualized by the Management System in a new browser tab and support SSH, RDP and VNC protocols.
- Remote tunnels are connections that are established from the local workstation to a target, similar to a VPN connection. They allow access to services and servers on the target from the user's local workstation. Remote tunnels are managed and established in the Nerve Connection Manager application and the Management System. The locally opened connection endpoint can then be used in a web browser, with SSH clients, or with remote desktop applications, depending on the target.
The targets of these remote connections can be nodes, workloads or external devices, which can be accessed from the node through the network.
Remote connections to workloads can be defined in existing workloads. Note that a workload does not have to be deployed again if a remote connection has been added. Defining a remote connection to a workload adds the remote connection to the workload across the Management System, meaning that it will also be available if the workload has already been deployed to nodes.
Select Remotes in the navigation on the left to view a list of currently established remote connections.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Search bar (1) | Use the search bar to filter remote connections by name or serial number. |
| CONNECTION NAME (2) | This is the name of the remote connection that is defined when the remote connection is configured. |
| TARGET (3) | This is the target of the remote connection. Note that this is not the name of the node. The hostname that was defined in the remote connection configuration is displayed here. |
| SERIAL NUMBER (4) | This is the serial number of the node to which the remote connection was established. In case of remote connections to workloads, the serial number of the node will be displayed to which the workload was deployed. For remote connections to external devices, the serial number of the node that the external device is connected to will be displayed. |
| USER (5) | This shows which user is using the established remote connection. If the same remote connection is used by two users, the remote connection will be listed again with a different user in te User column. |
| Ellipsis menu (6) | Clicking here opens an overlay that allows terminating connections. |
Note
- Note that the list of active remote connections is not updated in real-time. Refresh the page to see changes.
-
If a node goes offline while a remote connection is established, a cloud symbol will be displayed next to the remote connection to indicate that the connection to the node is interrupted.
Remote screens
A remote screen is established from the Management System to the target. It is opened in a new tab in the used web browser as soon as the remote connection is established.
Below are instructions on how to create SSH, VNC and RDP connections to nodes and workloads in the Management System.
Note
If the target of the remote connection is the host of the Nerve Blue system, use the IP address of the host: 172.20.2.1. Using localhost is not supported.
Configuring an SSH connection to a node
An SSH connection to a node can be used for accessing the host operating system of the node or an external device connected to the node that is reachable through an SSH connection.
- Select Nodes from the navigation on the left.
- Select the nodes tab
 on the right to display the list of registered nodes.
on the right to display the list of registered nodes. -
Select a node from the list to which a remote connection will be established.
-
Click Add Remote Screen under REMOTE CONNECTIONS on the right side.
-
Enter a name for the remote connection in the new window.
Note
Make sure to use a unique name for every connection on a node to avoid confusion.
-
Select SSH from the drop-down menu under Connection type.
- Enter the port used for SSH connection. The default port
22is automatically filled in. -
Enter the remaining information if applicable:
NERVE PARAMETERS Number of connections
Enter the maximum number of simultaneous connections. The default value is1.
Local acknowledgment
Select Yes or No from the drop-down menu.
Selecting Yes will require approval of the remote connection in the Local UI before the connection can be established. If No is selected, the settings in the Local UI do not apply.
Refer to Approving a remote connection for information on how to approve remote connections in the Local UI.NETWORK PARAMETERS Hostname
Enter the IP address or the hostname of the target here.
Autoretry
Set the number of retries if the remote connection fails. The default value is1.DISPLAY SETTINGS The display settings offer configuration options that affect visualization.
Swap red blue
If colors appear to not be displayed correctly, select true from the drop-down menu. This can occur when using VNC servers. Select false otherwise.
Cursor
This setting determines if the cursor is rendered locally or remotely. Enterlocalfor a local cursor or enterremotefor a remote cursor. If set toremote, the mouse pointer will be rendered remotely, and the local position of the mouse pointer will be indicated by a small dot. A remote mouse cursor will have added input lag compared to a local cursor. However, a remote cursor might be necessary if the server does not support sending the cursor image to the client.
Read only
Select true or false from the drop-down menu.
If set to true, no input will be accepted on the connection. Select false to allow input.AUTHENTICATION Enter Username and Password or tick the checkbox next to Private key authentication to use a private SSH key.
Note that ticking the checkbox changes the interface. Enter the username and choose one of the methods to add the private SSH key:- Click Choose File to open the local file browser and select the private SSH key file.
- Drag and drop the private SSH key file into the dotted line box saying Drop Private Key Here.
- Copy the private SSH key and paste it into the empty input field.
-
Select Save to add the remote connection.
The connection is now displayed under REMOTE CONNECTIONS on the right side, showing the NAME, TYPE and PORT of the remote connection.
Configuring a VNC connection to a node
A VNC connection to a node can be used to connect to a Linux environment on an external device, which is connected to the node or to the same network that the node is connected to.
- Select Nodes from the navigation on the left.
- Select the nodes tab
 on the right to display the list of registered nodes.
on the right to display the list of registered nodes. -
Select a node from the list to which a remote connection will be established.
-
Click Add Remote Screen under REMOTE CONNECTIONS on the right side.
-
Enter a name for the remote connection in the new window.
Note
Make sure to use a unique name for every connection on a node to avoid confusion.
-
Select VNC from the drop-down menu under Connection type.
- Enter the port used for VNC connection. The default port
5900is automatically filled in. -
Enter the password that was set for VNC connections at the target.
Note
Entering wrong login credentials will cause an error when the remote screen is established. If an error occurs, close the browser tab. Check the login credentials and re-establish the remote screen.
-
Enter the remaining information if applicable:
NERVE PARAMETERS Number of connections
Enter the maximum number of simultaneous connections. The default value is1.
Local acknowledgment
Select Yes or No from the drop-down menu.
Selecting Yes will require approval of the remote connection in the Local UI before the connection can be established. If No is selected, the settings in the Local UI do not apply.
Refer to Approving a remote connection for information on how to approve remote connections in the Local UI.NETWORK PARAMETERS Hostname
Enter the IP address or the hostname of the target here.
Autoretry
Set the number of retries if the remote connection fails. The default value is1.DISPLAY SETTINGS The display settings offer configuration options that affect visualization.
Swap red blue
If colors appear to not be displayed correctly, select true from the drop-down menu. This can occur when using VNC servers. Select false otherwise.
Cursor
This setting determines if the cursor is rendered locally or remotely. Enterlocalfor a local cursor or enterremotefor a remote cursor. If set toremote, the mouse pointer will be rendered remotely, and the local position of the mouse pointer will be indicated by a small dot. A remote mouse cursor will have added input lag compared to a local cursor. However, a remote cursor might be necessary if the server does not support sending the cursor image to the client.
Read only
Select true or false from the drop-down menu.
If set to true, no input will be accepted on the connection. Select false to allow input. -
Select Save to add the remote connection.
The connection is now displayed under REMOTE CONNECTIONS on the right side, showing the NAME, TYPE and PORT of the remote connection.
Configuring an RDP connection to a node
An RDP connection to a node can be used to connect to a Windows environment on an external device, which is connected to the node or to the same network that the node is connected to.
- Select Nodes from the navigation on the left.
- Select the nodes tab
 on the right to display the list of registered nodes.
on the right to display the list of registered nodes. -
Select a node from the list to which a remote connection will be established.
-
Click Add Remote Screen under REMOTE CONNECTIONS on the right side.
-
Enter a name for the remote connection in the new window.
Note
Make sure to use a unique name for every connection on a node to avoid confusion.
-
Select RDP from the drop-down menu under Connection type.
- Enter the port used for RDP connection. The default port
3389is automatically filled in. -
Enter the remaining information if applicable:
NERVE PARAMETERS Number of connections
Enter the maximum number of simultaneous connections. The default value is1.
Local acknowledgment
Select Yes or No from the drop-down menu.
Selecting Yes will require approval of the remote connection in the Local UI before the connection can be established. If No is selected, the settings in the Local UI do not apply.
Refer to Approving a remote connection for information on how to approve remote connections in the Local UI.NETWORK PARAMETERS Hostname
Enter the IP address or the hostname of the target here.
Autoretry
Set the number of retries if the remote connection fails. The default value is1.
Security mode
This mode dictates how data will be encrypted and what type of authentication will be performed, if any. Select an option from the drop-down menu. Possible values are:- ANY
This is the default if the field is left blank. Automatically select the security mode based on the security protocols supported by both the client and the server. - NLA (Network Level Authentication)
This mode uses TLS encryption and requires the username and password to be given in advance. Unlike RDP mode, the authentication step is performed before the remote desktop session actually starts, avoiding the need for the Windows server to allocate significant resources for users that may not be authorized. - RDP encryption
This is the standard RDP encryption. It is generally only used for older Windows servers or in cases where a standard Windows login screen is desired. Newer versions of Windows have this mode disabled by default and will only accept NLA unless explicitly configured otherwise. - TLS encryption
Select this for RDP authentication and encryption implemented via TLS (Transport Layer Security). The TLS security mode is primarily used in load balanced configurations where the initial RDP server may redirect the connection to a different RDP server.
If checked, the certificate returned by the server will be ignored, even if that certificate cannot be validated. This is useful if the server and the connection to the server is universally trusted, and if the server's certificate cannot be validated (for example, if it is self-signed).DISPLAY SETTINGS The display settings offer configuration options that affect visualization.
Swap red blue
If colors appear to not be displayed correctly, select true from the drop-down menu. This can occur when using VNC servers. Select false otherwise.
Cursor
This setting determines if the cursor is rendered locally or remotely. Enterlocalfor a local cursor or enterremotefor a remote cursor. If set toremote, the mouse pointer will be rendered remotely, and the local position of the mouse pointer will be indicated by a small dot. A remote mouse cursor will have added input lag compared to a local cursor. However, a remote cursor might be necessary if the server does not support sending the cursor image to the client.
Read only
Select true or false from the drop-down menu.
If set to true, no input will be accepted on the connection. Select false to allow input.AUTHENTICATION Enter Username and Password for Windows login.
Note that entering wrong login credentials will cause an error when the remote screen is established. If an error occurs, close the browser tab. Check the login credentials and re-establish the remote screen. - ANY
-
Select Save to add the remote connection.
The connection is now displayed under REMOTE CONNECTIONS on the right side, showing the NAME, TYPE and PORT of the remote connection.
Configuring a remote screen to a workload
A remote screen to a workload can be configured, regardless of a workload being deployed or not. Configuring a remote screen for a workload will immediately add the remote screen to the workload on all nodes that it has been deployed to. Note that remote screens to CODESYS workloads cannot be established.
- Select Workloads in the navigation on the left.
-
Select a workload from the list.
-
Select the workload version to which the remote connection will be added.
Note
Note that the configured remote connection will only be available for the version that was selected.
-
Click Add Remote Screen under REMOTE CONNECTIONS on the right side.
-
Follow steps 4 to 9 in the instructions above for SSH, VNC, or RDP connections.
Note
Note that adding the hostname is not required when configuring a remote screen to a Docker workload. The system automatically detects the hostname when the workload is deployed.
In case of Virtual Machine workloads, the hostname entry is not displayed for VNC connections. For SSH and RDP connections, enter the IP address or hostname under VM hostname / IP.
The connection is saved and now displayed under REMOTE CONNECTIONS on the right side, showing the NAME, TYPE and PORT of the remote connection.
Using a remote screen to a node or external device
Established remote screens are listed under Remotes in the navigation on the left until they are terminated.
- Select Nodes in the navigation on the left.
- Select the node tree tab
 on the right to display registered nodes in the node tree.
on the right to display registered nodes in the node tree. - Select a node with a remote screen from the node tree.
-
Click CONNECT in the node details on the right.
-
Select the remote connection from the list in the new window.
The remote screen will be opened and displayed in a new browser tab after a few seconds if Local acknowledgement has been set to No. If set to Yes, the remote connection has to be approved in the Local UI. Refer to Approving a remote connection for more information.
Note
Make sure not to exceed the defined number of connections of the same remote screen. This causes an error and the connection has to be terminated and established again. If there is a connection error, close the tab, terminate and re-establish the connection.
Using a remote screen to a workload
Established remote screens are listed under Remotes in the navigation on the left until they are terminated.
- Select Nodes in the navigation on the left.
- Select the node tree tab
 on the right to display registered nodes in the node tree.
on the right to display registered nodes in the node tree. - Select the node that has a deployed workload with a remote connection.
-
Select the workload.
-
Click CONNECT next to the workload status.
-
Select the remote connection from the list in the new window.
The remote screen will be opened and displayed in a new browser tab after a few seconds if Local acknowledgement has been set to No. If set to Yes, the remote connection has to be approved in the Local UI. Refer to Approving a remote connection for more information.
Note
Make sure not to exceed the defined number of connections of the same remote screen. This causes an error and the connection has to be terminated and established again. If there is a connection error, close the tab, terminate and re-establish the connection.
Remote tunnels
The Nerve Connection Manager is an application that is installed locally on the workstation. It is required for establishing and using remote connections from the local workstation. Download the Nerve Connection Manager from the Nerve Software Center first.
The Nerve Connection Manager installation file is an executable file. Open the installation file and follow the installation process. The filename of the installation file is Nerve Connection Manager Setup <version>.exe on Windows or Nerve Connection Manager Setup <version>.deb on Linux.
Once installed, the Nerve Connection Manager will be associated with nerverm:// links that are generated in the Management System. Clicking such a link will automatically open the Nerve Connection Manager.
Note
If the target of the remote connection is the host of the Nerve Blue system, use the IP address of the host: 172.20.2.1. Using localhost is not supported.
Compatibility of the Nerve Connection Manager
Make sure that the correct version of the Nerve Connection Manager is installed according to the version of the Management System that is used:
| Management System | Nerve Connection Manager |
|---|---|
| v2.2.X | v1.0.2 |
| v2.1.X | v1.0.1 |
| v2.1.0 | v1.0.0 |
Configuring a remote tunnel to a node
Depending on the target, a remote tunnel to a node can be used in a web browser, with SSH clients, or with remote desktop applications, for example.
- Select Nodes in the navigation on the left.
- Select the nodes tab
 on the right to display the list of registered nodes.
on the right to display the list of registered nodes. -
Select a node from the list.
-
Select Add Remote Tunnel under REMOTE CONNECTIONS on the right side.
-
Enter the following information:
NERVE PARAMETERS Name
Enter a name for the remote connection. Make sure to use a unique name for every connection on a node to avoid confusion.
Local acknowledgment
Select Yes or No from the drop-down menu.
Selecting Yes will require approval of the remote connection in the Local UI before the connection can be established. If No is selected, the settings in the Local UI do not apply.
Refer to Approving a remote connection for information on how to approve remote connections in the Local UI.NETWORK PARAMETERS Hostname
Enter the IP address or the hostname of the target here.
Port on node
Enter the port the target listens on.
Port on PC
Enter the port that will be used for communication on the local workstation. The port entered here serves as a default port that can be changed in the Nerve Connection Manager in case it is already in use. Note that some systems might restrict usage of ports under 1024. This is true for Linux systems especially. Enter port numbers higher than 1024 to avoid possible port conflicts. -
Select Save to save the remote connection configuration.
The connection is saved and now displayed under REMOTE CONNECTIONS on the right side, showing the NAME, TYPE and PORT of the remote connection.
Configuring a remote tunnel to a workload
A remote tunnel to a workload can be configured, regardless of a workload being deployed or not. Configuring a remote tunnel for a workload will immediately add the remote tunnel to the workload on all nodes that it has been deployed to. Depending on the target, a remote tunnel to a workload can be used in a web browser, with SSH clients, or with remote desktop applications, for example.
- Select Workloads in the navigation on the left.
-
Select a workload from the list.
-
Select the workload version to which a remote connection will be established.
Note
Note that the configured remote connection will only be available for the version that was selected.
-
Select Add Remote Tunnel under REMOTE CONNECTIONS on the right side.
-
Enter the following information:
NERVE PARAMETERS Name
Enter a name for the remote connection. Make sure to use a unique name for every connection on a node to avoid confusion.
Local acknowledgment
Select Yes or No from the drop-down menu.
Selecting Yes will require approval of the remote connection in the Local UI before the connection can be established. If No is selected, the settings in the Local UI do not apply.
Refer to Approving a remote connection for information on how to approve remote connections in the Local UI.NETWORK PARAMETERS Port on node
Enter the port the target listens on.
Port on PC
Enter the port that will be used for communication on the local workstation. The port entered here serves as a default port that can be changed in the Nerve Connection Manager in case it is already in use. Note that some systems might restrict usage of ports under 1024. This is true for Linux systems especially. Enter port numbers higher than 1024 to avoid possible port conflicts.Note
Note that adding the hostname is not required when configuring a remote tunnel to a Docker workload. The system automatically detects the hostname when the workload is deployed.
For CODESYS workloads, the Hostname and Port on node fields are filled in by the default. They contain the IP address and default port of the CODESYS runtime.
-
Select Save to save the remote connection configuration.
The connection is saved and now displayed under REMOTE CONNECTIONS on the right side, showing the NAME, TYPE and PORT of the remote connection.
Using a remote tunnel to a node or external device
Note that the Nerve Connection Manager is required to use a remote tunnel. Download the Nerve Connection Manager from the Nerve Software Center and install it first.
Established remote tunnels are listed under Remotes in the navigation on the left until they are terminated.
- Select Nodes in the navigation on the left.
- Select the node tree tab
 on the right to display registered nodes in the node tree.
on the right to display registered nodes in the node tree. - Select a node with a remote tunnel from the node tree.
-
Click CONNECT in the node details on the right.
-
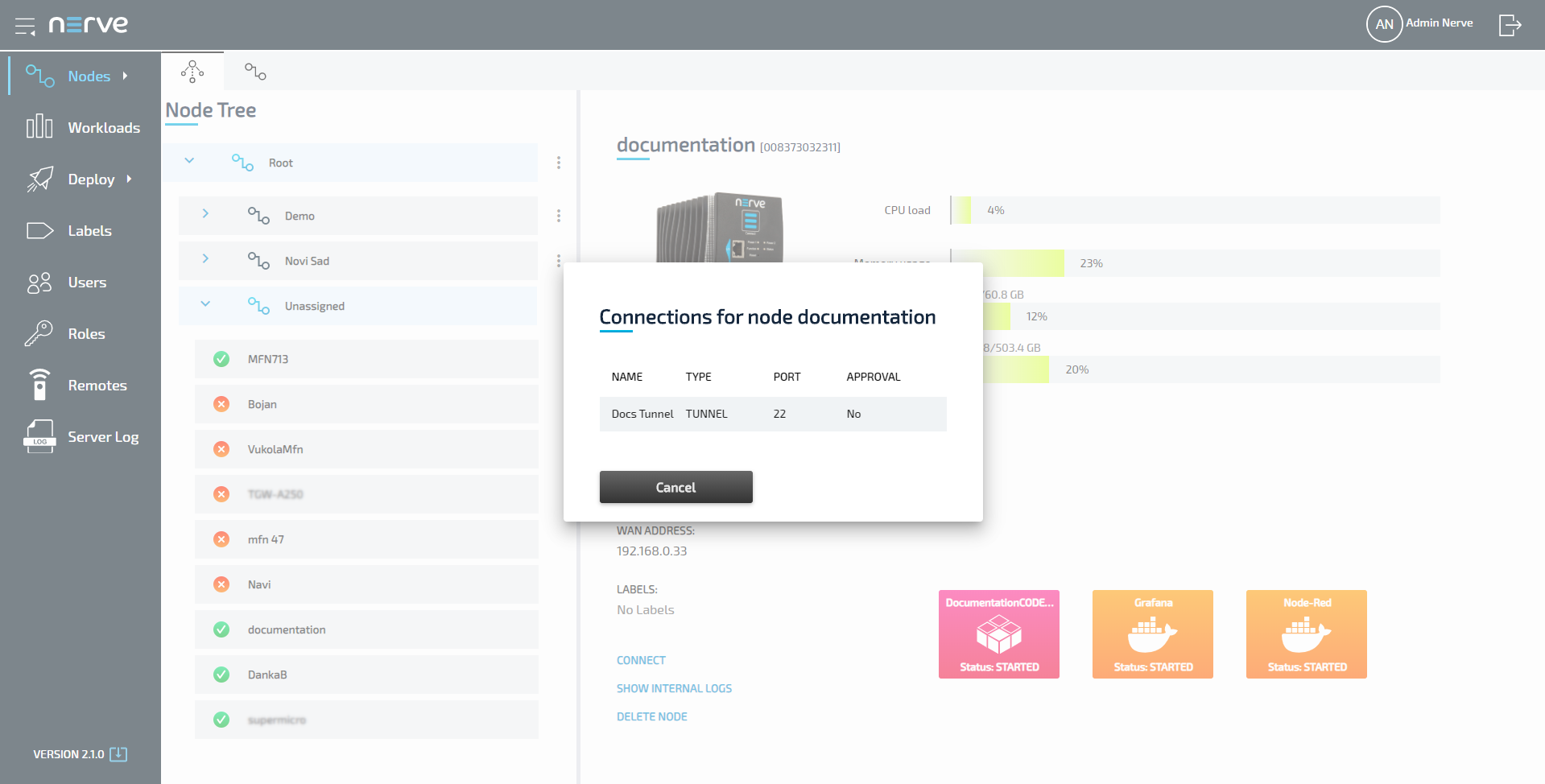
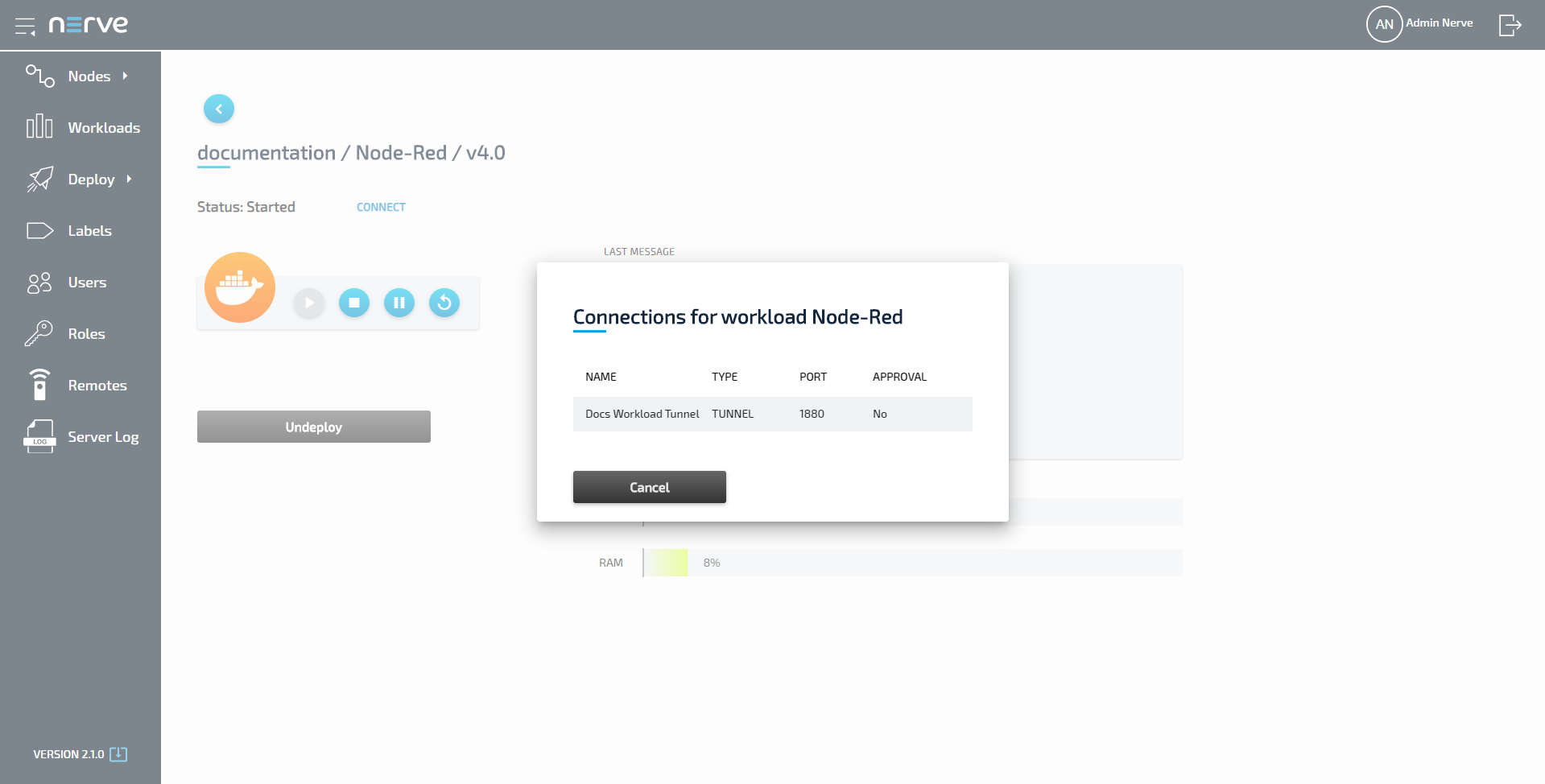
Select the remote connection from the list in the new window. Note that remote tunnels have the type TUNNEL.
-
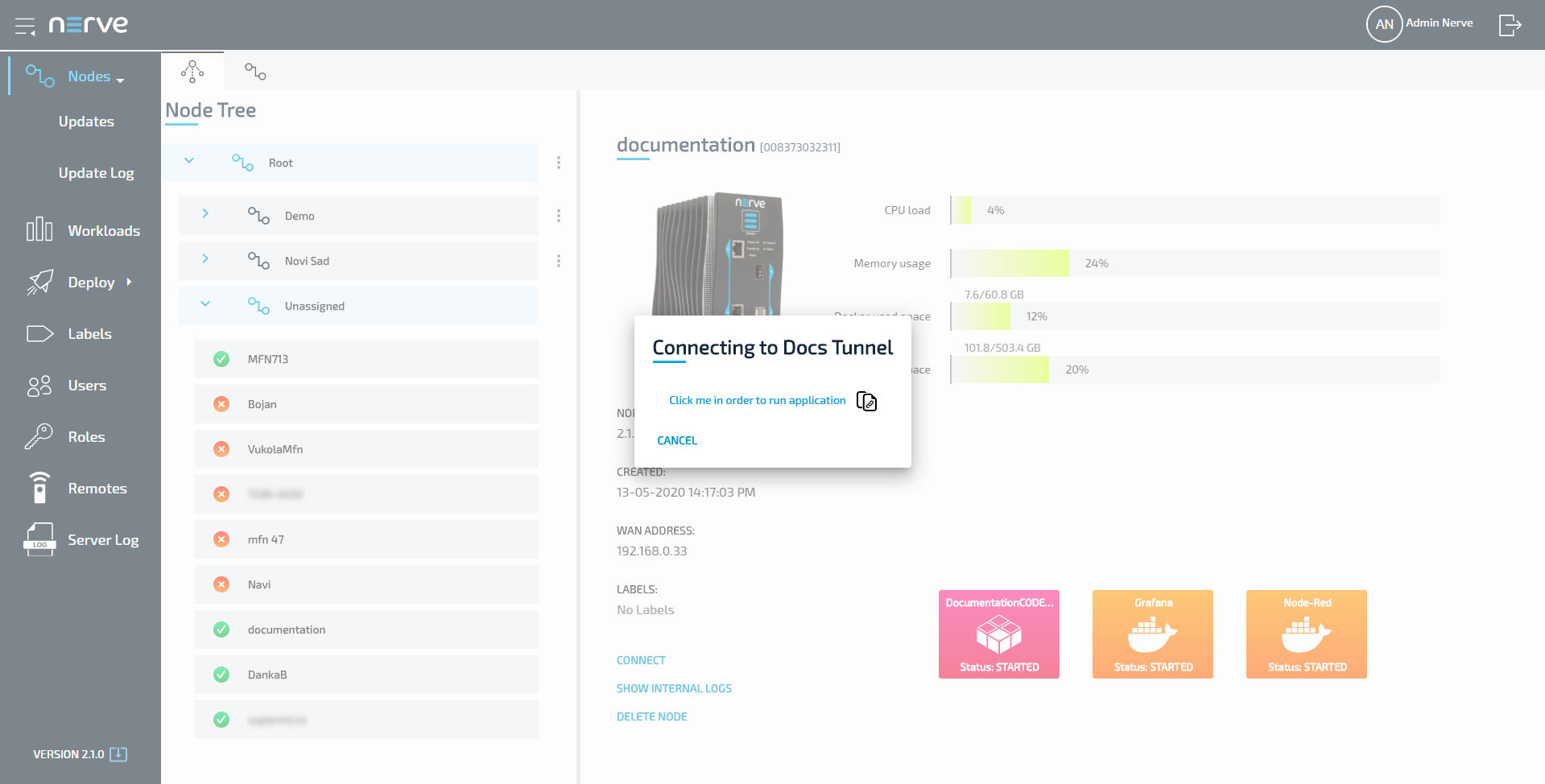
Select Click me in order to run application in the new window.
Note
If Local acknowledgment is set to Yes, the Management System will wait for approval until the remote connection has been locally approved before displaying the window above. Refer to Approving a remote connection for more information.
-
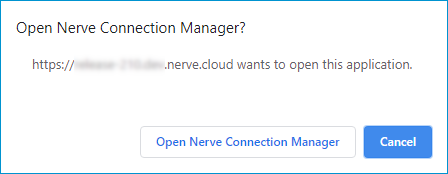
If the Nerve Connection Manager installed correctly, confirm the browser message that the Nerve Connection Manager shall be opened.
Depending on the browser that is used, this message will differ. The Nerve Connection Manager will start automatically once the message is confirmed.Note
If the Nerve Connection Manager does not start automatically, select the copy to clipboard symbol next to Click me in order to run application in the Management System. This copies the remote connection URL.
Start the Nerve Connection Manager manually and add the new connection by clicking ADD NEW CONNECTION in the lower right and pasting the URL.
If an established connection already exists in the Nerve Connection Manager, select the Add new connection symbol next to Connections on the left side of the window.
The remote connection will be established once the Nerve Connection Manager starts.
Data about the establish remote tunnel is displayed on the right half of the Nerve Connection Manager window, showing the Status, Connection target, Remote port and Local port with a summary on the left side under the remote tunnel name.
Note
If the local port on the local workstation is already in use or occupied by the system, the Nerve Connection Manager will not establish a connection. Local port will be marked on the right. Enter a different port in this field that is not used on the workstation in order to establish the remote tunnel.
The connection can now be used from the local workstation by using localhost:<localport> through PuTTY in order to establish an SSH connection or in a web browser. The screenshot below shows how to connect to a node through a remote tunnel using the CODESYS Development System. In an open project, double-click Device (Nerve_MFN_100) in the tree view on the left. Go to Communication Settings in the middle of the window and enter 127.0.0.1:<portonpc> in the text box under the device on the right. Replace <portonpc> with the port number that was defined under Port on PC in the Management System.
Disconnect from the remote tunnel by clicking DISCONNECT in the lower right corner of the Nerve Connection Manager.
Note
Alternatively, all remote connections can be disconnected at once by clicking the Disconnect all symbol on the left side next to Connections.
Note that disconnecting does not terminate the connection. The connection will stay established until it is terminated in the Nerve Connection Manager, the Local UI or the Management System.
Using a remote tunnel to a workload
Note that the Nerve Connection Manager is required to use a remote tunnel. Download the Nerve Connection Manager from the Nerve Software Center and install it first.
Established remote tunnels are listed under Remotes in the navigation on the left until they are terminated.
- Select Nodes in the navigation on the left.
- Select the node tree tab
 on the right to display registered nodes in the node tree.
on the right to display registered nodes in the node tree. - Select the node that has a deployed workload with a remote connection.
-
Select the workload.
-
Click CONNECT next to the workload status.
-
Select the remote connection from the list in the new window. Note that remote tunnels have the type TUNNEL.
-
Select Click me in order to run application in the new window.
Note
If Local acknowledgment is set to Yes, the Management System will wait for approval until the remote connection has been locally approved before displaying the window above. Refer to Approving a remote connection for more information.
-
If the Nerve Connection Manager installed correctly, confirm the browser message that the Nerve Connection Manager shall be opened.
Depending on the browser that is used, this message will differ. The Nerve Connection Manager will start automatically once the message is confirmed.Note
If the Nerve Connection Manager does not start automatically, select the copy to clipboard symbol next to Click me in order to run application in the Management System. This copies the remote connection URL.
Start the Nerve Connection Manager manually and add the new connection by clicking ADD NEW CONNECTION in the lower right and pasting the URL.
If an established connection already exists in the Nerve Connection Manager, select the Add new connection symbol next to Connections on the left side of the window.
The remote connection will be established once the Nerve Connection Manager starts.
Data about the establish remote tunnel is displayed on the right half of the Nerve Connection Manager window, showing the Status, Connection target, Remote port and Local port with a summary on the left side under the remote tunnel name.
Note
If the local port on the local workstation is already in use or occupied by the system, the Nerve Connection Manager will not establish a connection. Local port will be marked on the right. Enter a different port in this field that is not used on the workstation in order to establish the remote tunnel.
The connection can now be used from the local workstation by using localhost:<localport> through PuTTY in order to establish an SSH connection or in a web browser. Disconnect by clicking DISCONNECT in the lower right corner.
Note
Alternatively, all remote connections can be disconnected at once by clicking the Disconnect all symbol on the left side next to Connections.
Note that disconnecting does not terminate the connection. The connection will stay established until it is terminated in the Nerve Connection Manager, the Local UI or the Management System.
Terminating remote connections
Remote connections are open and can be used as long as they are not terminated. A remote connection can be terminated from the Management System, in the Local UI or in the Nerve Connection Manager. Also, remote connections terminate automatically after 30 minutes of inactivity. Once a connection has been terminated, it has to be established again.
Terminating an active remote connection in the Management System
Note that terminating an open remote connection does not remove the configuration of the remote connection from the node or workload. If a remote connection is terminated, it has to be re-established in the Management System to be used again.
- Connect to the Management System.
- Select Remotes in the navigation on the left.
- Select the ellipsis menu to the right of an active remote connection.
-
Select TERMINATE in the overlay that appeared.
-
Select OK in the new window.
Terminating a connection in the Management System automatically removes the connection in the Management System, Local UI and Nerve Connection Manager.
Note
Once a remote screen has been terminated while the browser tab is still open, a pop-up window will appear that offers the option to reconnect. Clicking Reconnect in the pop-up window has no effect. Close the window and re-established the connection in the Management System.
Terminating an active remote connection in the Local UI
Note that terminating an open remote connection does not remove the configuration of the remote connection from the node or workload. If a remote connection is terminated, it has to be re-established in the Management System to be used again.
- Connect to the Local UI.
- Select Remote Connections in the navigation on the left.
- Choose the remote connections that will be terminated.
-
Select Disconnect.
-
Select YES in the new window.
Terminating a connection in the Local UI automatically removes the connection in the Management System, Local UI and Nerve Connection Manager.
Terminating a remote connection in the Nerve Connection Manager
Note that terminating an open remote connection does not remove the configuration of the remote connection from the node or workload. If a remote connection is terminated, it has to be re-established in the Management System to be used again.
- Open the Nerve Connection Manager. Note that the Nerve Connection Manager will already be open if a remote tunnel has been established.
- Select a remote connection that will be terminated in the list on the left.
-
Select REMOVE in the lower-right.
-
Select YES in the overlay that appeared.
Terminating a connection in the Nerve Connection Manager automatically removes the connection in the Management System, Local UI and Nerve Connection Manager. Exiting the Nerve Connection Manager terminates all remote tunnels
Common error cases and known issues
Below is a list of most common error cases and known limitations. Hints how to avoid them or solve them the easiest way are given where applicable.
Remote screens
-
When trying to connect to a suspended workload, long loading times might occur. The connection can also seem established but the user will not be able to act in the remote screen window. The reason might be that a remote screen to a suspended workload was attempted. This is not supported.
Close the browser tab and terminate the connection in the Management System in that case. Make sure the workload is in the started state and re-establish the remote screen. If the behavior persists, investigate the workload settings or the node.
-
Remote screens to workloads will be shown as active under Remotes if the workload is undeployed while the remote screen is being used.
Remote tunnels
-
Using two remote tunnels to two nodes, accessing the Local UI of each node at the same time is not possible. This is due to authentication conflicts.
Use the incognito mode of the current browser for the second tab or a second browser if both Local UIs have to be operated at the same time.
-
Some systems might restrict usage of local ports lower than 1024. This is true for Linux systems especially. Enter ports higher than 1024 under Port on PC when configuring a remote tunnel to avoid port conflicts.